Resources & Tools
Everything you need to succeed.
Centrifuge Tools
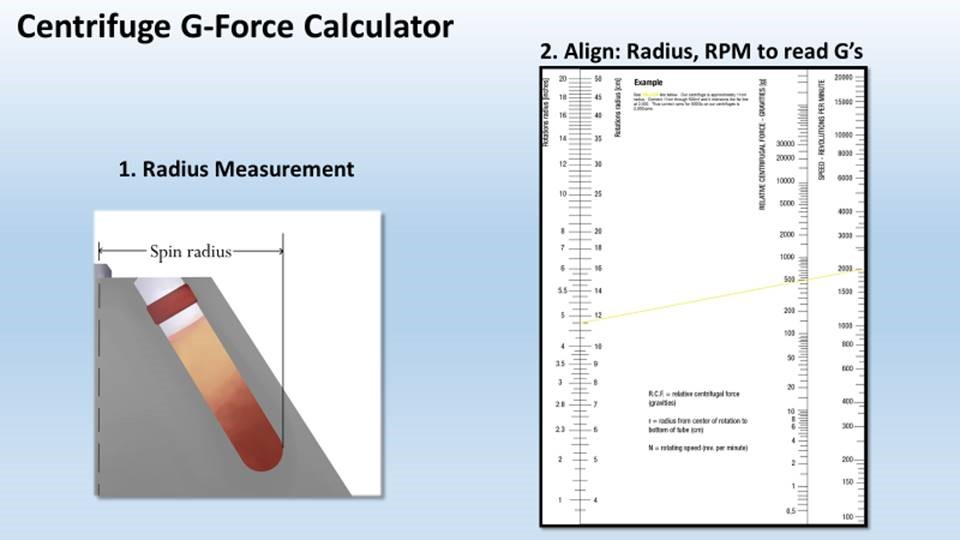
Instructions For Converting RCF (G-Force) to RPM:
- Refer to centrifuge manual or measure the spin radius by holding a ruler parallel to the counter top and measuring the horizontal distance from center of rotation — usually a bolt in the middle of the rotor — to the far tip of a bucket
- Enter this in the “Rotor Radius” field
- Enter the desired RCF (aka G-Forces)
- Hit “Calculate RPM”
- Read the number that appears in the “RPM” box and use this setting on your centrifuge
Centrifuge Radius Measurement Instructions
Open Image >>
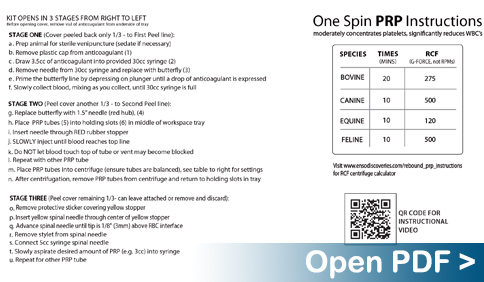
PRP Spin Composition
Open PDF >>

Rotor Calculator

COREY ORAVA, DVM
ENSO DISCOVERIES PRESENTS
REBOUND PRP & PRF: WHAT MAKES PLATELETS AND PLASMA SO SPECIAL?
Regenerative medicine for veterinary teams presented by Enso’s Chief Scientific Officer and Rebound Inventor Corey Orava, DVM.
Rebound™ PRP Kit Support Material
Rebound™ PRP Kit Instructions
Rebound™ PRP Product Detailer
Rebound™ PRP White Paper
Rebound™ PRP Case Studies
Rebound™ PRF Kit Support Material
Rebound™ PRF Kit Instructions
Rebound™ PRF Product Detailers
Rebound™ PRF White Paper
Rebound™ PRF Case Studies
Invoice Examples
Small Animal Resource Library
Injection Aid Videos
Injection Aid Video
Elbow Injection
Hip Joint Injection
Shoulder Injection
Injection Aids
Open PDF >
Small/cat 23ga 1” 1 ml Medium 22ga 1.5” 1.0 – 1.5 ml Large 22ga 2.5” 1.5 – 2.0 ml Giant 22ga 2.5” 2.0 – 3.0 ml
- Position animal on its’ back
- Palpate tip of patella and tibial tuberosity
- Palpate patellar tendon
- Insert needle beside (either medial or lateral) patellar tendon halfway between the tip of the patella and the tibial tuberosity
- Needle is started perpendicular to the skin, once through the skin angle sagittal (i.e. towards the midline) and proximal (see red arrow below)
- Advance the needle in one continuous motion until you hit bone (distal femur)
- In very small animals it is easy to pass the needle through the back of the joint space – angling the needle proximal should prevent this
Open PDF >
Small/cat 25ga 1” … 0.5 ml Medium 23ga 1.5” …
- Cat/dog in lateral recumbency
- palpate spine of scapula, follow to acromion process (absent in feline)
- insert needle about 0.5 to 1cm distal to acromion process (refer to lateral x-rays:
- measure distance from tip of process to joint space)
- needle inserted vertically (perpendicular to table) and in-line with spine of scapula
Open PDF >
Small/cat 25ga 1” 0.5 ml Medium 23ga 1” 0.5 – 1.0 ml Large 22ga 1.5” 1.0 – 1.5 ml Giant 22ga 2.5” 1.5 – 2.0 ml
- Can be done medially or laterally
- 3 approaches for each side (same landmarks whether medial or lateral)
- Alternative is to practice with skeleton model – fold towel over a few times, lay folded towel over model and inject joint through the towel
- 1st approach – inject distal to epicondyle (black circle), in 50lb dog typically would be about 1cm from the middle of the epicondyle (can measure distance on x-rays), place rolled towel (or similar) under humerus to help open joint space, needle vertical or hub tilted slightly (15*) towards paw, use a small gauge needle (e.g. 25ga – 1”) and walk needle into joint space – joint fluid not common
- 2nd approach – inject between epicondyle and point of olecranon (closer to olecranon), palpate for neurovascular bundle and insert needle beside (usually needle is caudal to nerve), needle angled about 45o (hub towards point of olecranon), visualize a 2-D plane that passes through epicondyle and point of olecranon – keep the tip of the needle AND the hub of the needle in this plane, the needle follows olecranon into joint space – joint fluid more common
- 3rd approach – ONLY do if animal is comfortable placing elbow in full flexion. Needle is insert just proximal to olecranon processes then inserted toward the middle of the joint, directly under the epicondyle
Open PDF >
Small/cat 23ga 1” 1 ml Medium 22ga 1.5” 1.0 – 1.5 ml Large 22ga 2.5” 1.5 – 2.0 ml Giant 22ga 2.5” 2.0 – 3.0 ml
Animal in lateral recumbency with leg approximately perpendicular to spine
- Place finger tips on greater trochanter (GT)
- Walk finger tips towards spine until index finger falls off end
- Insert needle off end of GT
- Aspirate for fluid or attempt to inject
- If joint is not encountered, walk needle tip towards GT then away from GT